Pipeline Flow and Examples¶
Foremast generates a single pipeline per region. The pipeline is designed to allow deploying to multiple environment with checkpoints between each transition.
Default Pipeline Flow¶
The below flow can repeat for as many environments as defined in the configs. In general, most applications repeat a common set of stages 2-3 times. Typically, the same way to deploy to dev (if used), stage, and production.
- Configuration
- This stages defines the Jenkins trigger, property files, and pipeline-wide notifications
- Bake
- Bakes an AMI the specified AMI ID
- Infrastructure Setup [$env]
- Calls a Jenkins job to run the
prepare-infrastructureForemast command against a specific account. - Setups AWS infrastructure such as ELB, IAM roles, S3 bucket, and DNS needed for an application
- Calls a Jenkins job to run the
- Deploy $env
- Uses Spinnaker to create a cluster and server group in specific account.
- The behavior of this stage is largely based on the application-master-$account.json configs.
- Attach Scaling Policy [$env]
- If a scaling policy is defined in application-master-$account.json, attaches it to the deployed server group
- If no policy is defined, this stage is excluded
- Checkpoint $next-env
- A manual checkpoint stage. This requires human intervention to approve deployment to the next environment.
Stages 3-6 repeat for each environment/account defined in pipeline.json.
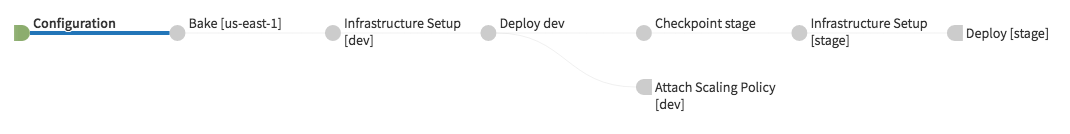
The default generated pipeline should look like the above image. This is the basic bake -> infrastructure -> deploy -> checkpoint pipeline described above.
Custom Pipelines¶
You can specify an external templates directory in foremast.cfg / config.py. Templates in an external directory will need to have the same directory structure and naming as the default templates. if templates_path is set in foremast.cfg / config.py, Foremast will first see if the file exists there. If not, it will fall back to the provided templates.
If you need to add more stages or change the defaults, this is all possible via external templates. Please the foremast-templates repo for examples on the templates.
Example Workflow¶
Most Foremast users have a detailed workflow for using Foremast internally. Feel free to copy this example workflow or use it as inspiration for your own. You can view all of our internal templates on the foremast-templates repo.
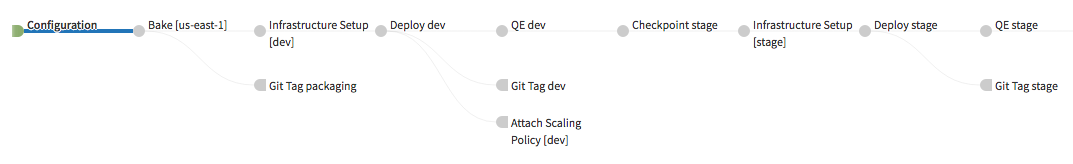
- The application-master-$account.json and pipeline.json are bundled directly with the application code
- Developer makes a change to one of those configs and pushes to the application’s git repository
- A server-side git hook detects a change and triggers a Jenkins job to run
Foremast
prepare-app-pipeline- Regenerates the application and pipeline in Spinnaker
- Build application artifacts using a Jenkins job and stored as an RPM
- Spinnaker triggers detect a completed Jenkins job and starts a new deployment
pipeline
- Bake an AMI using built RPM
- Jenkins Stage runs Foremast
prepare-infrastructure- Creates the AWS ELB, SG, S3 bucket, and IAM roles
- Jenkins Stage tags the source repository with AMI info
- Deploy the generated AMI to desired environments
- Jenkins Stage runs Quality Engineering tests against deployed application
- Jenkins Stage tags the source repository with deployment information
- Jenkins Stage attaches defined scaling policies
- Manual judgment before continuing to the next environment